Magento vs. WooCommerce: Do They Have Any Reason for Competition
Categorized as : Ecommerce
The ecommerce software market is changing drastically clashing and stirring leaders and newcomers. Some platforms make tremendous spurts and leave us behind guessing, if it is just an accidental happening or rising of the new star.
WooCommerce is that black horse, which made us stand still in wonder, but really curious, if it has anything to do with ecommerce or more about blogging. In this post we’ll try to find out the differences of stores made on Magento and WooCommerce and their characteristics as possible competitors.
Study Description
This study explores Magento and WooCommerce based online stores extracted from the Alexa 1 million top web sites list and their particular features. It reveals the differences of the mentioned above site groups by languages, countries, ecommerce functionality, and commercial branches.
Randomly chosen from the parent population the study examines 1% size samples or about 300 web sites based on Magento CE, Magento EE, and WooCommerce. Magento CE and Magento EE are studied separately since their target audience and price models differ greatly, what makes their stores different, as a result.![]() We’d like to remind you that the data and analysis results are solely collected and interpreted by aheadWorks and can’t be considered beyond the context of this study.
We’d like to remind you that the data and analysis results are solely collected and interpreted by aheadWorks and can’t be considered beyond the context of this study.
The Study
Alexa Rankings
One of the most discussed topics within the Magento vs. WooCommerce dispute are their web site rankings and other measurements. Using Alexa ranks we’ve found, who is better and to what extent.
Diagram 1. Stores within 100 K Intervals of the Alexa Top 1 Mln Rating, %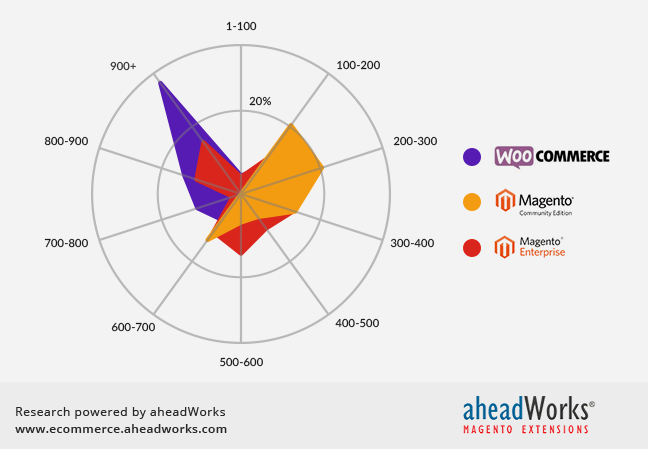
WooCommercу is really less successful and mostly takes positions from 700 thousand to 1 million. Magento CE is mostly equally spread along the chart positions, while Magento EE is largely situated within the 100-400 thousand positions range. However, on the average Magento CE and Magento EE are not so dramatically different with the 565 241 and 535 475 average positions, while WooCommerce takes only the 727 164th average place.
Product Types
35% of sites made on WooCommerce sell immaterial products and services, which is a significant share, not typical for Magento. And, software is the most frequent business line for WooCommerce based online stores.
Diagram 2. Stores by Product Types, %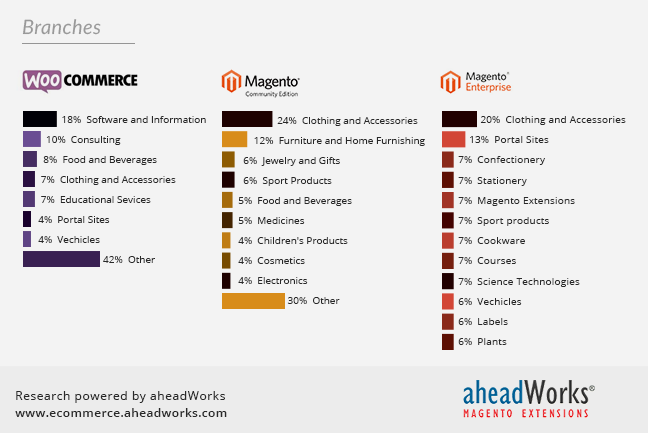
Magento CE seems to be greatly suitable for clothing stores, which take 24% of the pie. And, on the Magento CE diagram there is absolutely no sectors related to immaterial products.
Magento EE stores inherit mostly from successful brands rather than products and can hardly describe the average market situation. So, here we find both tangible and immaterial products and some unusual commercial fields like confectionery and stationery.![]() Findings. WooCommerce online stores sell immaterial products, while Magento CE is mostly oriented towards tangible goods.
Findings. WooCommerce online stores sell immaterial products, while Magento CE is mostly oriented towards tangible goods.![]() Potentials. All diagrams still miss some popular types of products traditionally successful in ecommerce: finance and insurance, travelling, music, and other virtual products. We didn’t see any of them in our samples, so these areas may be a great potential for Magento to win new customers.
Potentials. All diagrams still miss some popular types of products traditionally successful in ecommerce: finance and insurance, travelling, music, and other virtual products. We didn’t see any of them in our samples, so these areas may be a great potential for Magento to win new customers.
Countries
The structure of stores by countries also differs greatly. WooCommerce is popular in two main countries – United States and India. Many other essential segments belong to European countries and rarely to Asia or South America.
Diagram 3. Stores by Countries, %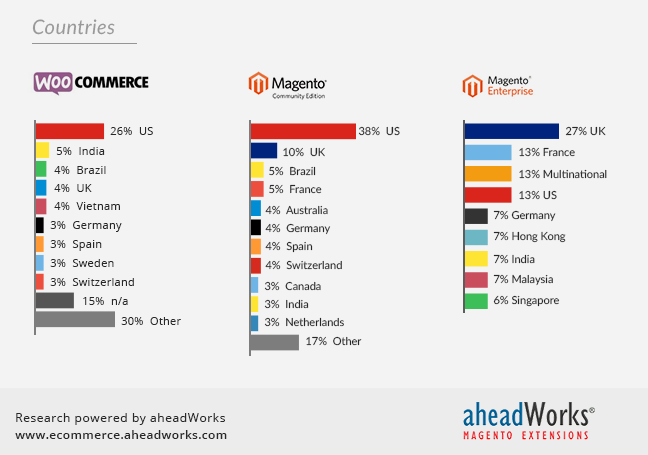
Meanwhile, Magento CE is popular in United States and United Kingdom, which take almost one half of all Magento CE based stores.
The specific features of the web sites made on Magento EE are the considerably big share of multinational sites and the second place of the United States within this group of analyzed stores. United Kingdom here is the obvious leader, while “Asian Tigers” Hong Kong and Malaysia take the fifth place in in this small competition.![]() Findings. Despite WordPress has never been considered to be an ideal platform for online sales, WooCommerce is popular in the U.S. and European countries. The geography of Magento CE is even more diversified and includes some Asian, South American, and Pacific countries.
Findings. Despite WordPress has never been considered to be an ideal platform for online sales, WooCommerce is popular in the U.S. and European countries. The geography of Magento CE is even more diversified and includes some Asian, South American, and Pacific countries.![]() Potentials. Currently, Asian countries make a great challenge. Malaysia, Indonesia, Hong Kong, Thailand, Singapore are often met in all tree samples of our study (WooCommerce, Magento CE and Magento EE), which illustrates that ecommerce is already common and has great potential there. Still, we miss some big global traders on our diagrams – Japan and China, the second and the fourth global merchandise traders, accordingly.
Potentials. Currently, Asian countries make a great challenge. Malaysia, Indonesia, Hong Kong, Thailand, Singapore are often met in all tree samples of our study (WooCommerce, Magento CE and Magento EE), which illustrates that ecommerce is already common and has great potential there. Still, we miss some big global traders on our diagrams – Japan and China, the second and the fourth global merchandise traders, accordingly.
Languages
English is expectedly is the most popular language of all platforms:
- WooCommerce – 61%;
- Maento CE – 65%;
- Magento EE – 73%.
Diagram 4. Stores by Languages, %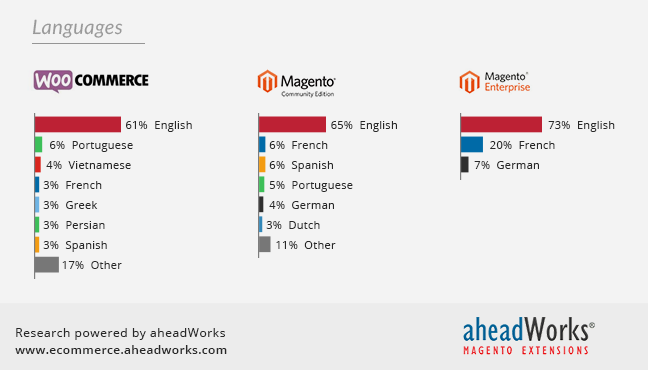
French is very popular in both Magento CE and Magento EE, while WooCommerce embraces some exotic languages like Vietnamese and Persian. Greeks also like WooCommerce pretty much.![]() Findings. English is the major language of ecommerce and contributes to the success of more than 60% of WooCommerce and Magento web stores.
Findings. English is the major language of ecommerce and contributes to the success of more than 60% of WooCommerce and Magento web stores.![]() Potentials. Just like in the countries list, we miss some significant global languages on our diagrams – Chinese, Hindi, Arabic, Japanese, and Javanese. Using native languages is a great advantage for the merchants trading in these countries.
Potentials. Just like in the countries list, we miss some significant global languages on our diagrams – Chinese, Hindi, Arabic, Japanese, and Javanese. Using native languages is a great advantage for the merchants trading in these countries.
Ecommerce Functionality
The most important thing about ecommerce solutions is their functionality and the possibilities to fully utilize it to make a profit. In our study we also explore the opportunity to put products into carts and calculate the number of web sites with broken or missing product baskets.
Diagram 4. Stores by Ecommerce Functionality, %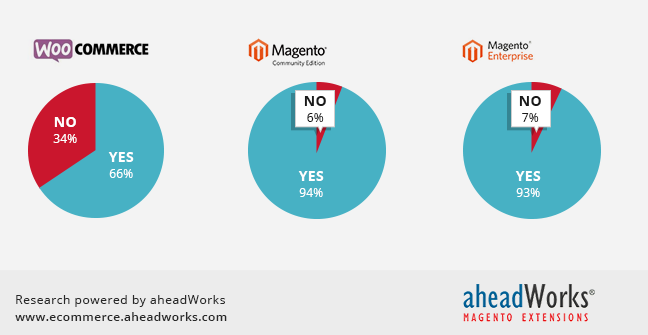
On the average, Magento CE and Magento EE have only 6% and 7% of sites with no ecommerce functionality. Usually, these web sites are multinational brands, which have local online stores or physical warehouses in each country of their activity. But, WooCommerce sites are much less keen to sell online and have 34% of sites without active carts.![]() Findings. Magento is used completely for ecommerce purposes, while WooCommerce web sites often do not use ecommerce features and keep it just in case, possibly.
Findings. Magento is used completely for ecommerce purposes, while WooCommerce web sites often do not use ecommerce features and keep it just in case, possibly.![]() Potentials. If WooCommerce web site owners are not satisfied with the provided functionality, other platforms can find here new users or customers. But, WooCommerce is also able to intensify the use of ecommerce features, especially that store owners have their plugin installed, already.
Potentials. If WooCommerce web site owners are not satisfied with the provided functionality, other platforms can find here new users or customers. But, WooCommerce is also able to intensify the use of ecommerce features, especially that store owners have their plugin installed, already.
Conclusion
Having behind WordPress WooCommerce started strongly, but needs some time for evolution to be a full-fledged member of the club.
Subjectively, the monetization of WooCommerce online stores is less sufficient compared to Magento stores. Magento seems to be more functionally matured, and WooCommerce is currently not able to replace it 100%. However, further expansion of these two platforms will inevitably push them together. Let’s wait.
Add your comments below, please.